
Understanding EDI in Circle K: A Comprehensive Guide
We recently wrote about why big retailers are forcing DSD companies to use EDI and DEX. The reason is that Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) is the backbone of a global convenience store chain that ensures smooth operations, accurate inventory management, and timely payments. We have talked about EDI and DEX in Walmart, Publix, and Kroger. In this article, I delve into the essentials of EDI in Circle K network, exploring its structure, requirements, and test procedures.
What is EDI?
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) is the electronic exchange of business documents between trading partners in a standardized format. It eliminates the need for paper-based communication, reduces errors, and speeds up transactions, making it an essential tool for modern retail operations.
The Role of EDI in Circle K
With its extensive network of stores and suppliers, Circle K relies on EDI to manage its supply chain efficiently. EDI facilitates the automated exchange of purchase orders, invoices, shipping notices, and other critical business documents, ensuring real-time communication between Circle K and its trading partners.
Circle K’s EDI Structure
EDI in Circle K system is structured to handle various types of transactions with its suppliers and partners. The EDI structure typically includes:
- Purchase Orders (850): Used to place orders for goods and services.
- Invoices (810): Sent by suppliers to request payment for goods shipped or services provided.
- Advanced Shipping Notices (856): Inform Circle K about the contents of a shipment before it arrives.
- Inventory Advice (846): Helps manage stock levels by providing up-to-date inventory data.
- Remittance Advice (820): Provides information on payments made.
Each of these documents follows specific formats and standards, such as ANSI X12 or EDIFACT, ensuring consistency and compatibility across different systems.
Requirements for EDI in Circle K Partners
To successfully integrate with EDI in Circle K system, suppliers must meet specific requirements:
- Compliance with EDI Standards: Partners must adhere to the required EDI standards (e.g., ANSI X12) for document formatting.
- Data Accuracy: Accurate and timely data submission is critical to avoid delays and errors in processing.
- Secure Communication: EDI transmissions should be secure, typically using protocols like AS2 or SFTP.
- Testing and Validation: Before going live, all EDI transactions must be thoroughly tested to ensure they meet Circle K’s standards.
EDI Test Procedures in Circle K
Circle K’s EDI test procedures are designed to validate the accuracy and reliability of data exchange before full integration. These procedures include:
- Connectivity Testing: Ensures the secure transmission of EDI documents between Circle K and its partners.
- Format Validation: Verifies that the EDI documents conform to the required standards and formats.
- Data Integrity Testing: Checks for accuracy and completeness of data in each document.
- End-to-End Testing: Simulates the entire EDI process, from document generation to receipt, to ensure seamless integration.
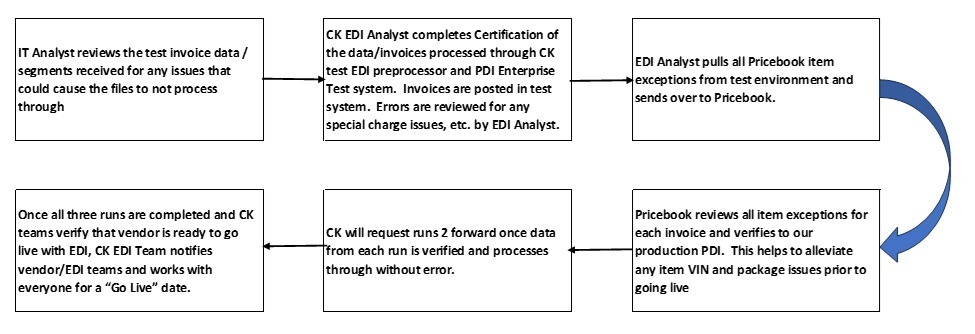
Testing consists of Three set of debits and credits (runs). Circle K will provide the Incoming Vendor Number to be used for EDI. CK reviews the store count to determine how many invoices will be needed to test in each run and that is given to vendor. Store information is to include the CK 7-digit store number. The graph illustrates the process
The Benefits of EDI for Circle K
Implementing EDI brings numerous benefits to Circle K and its trading partners:
Increased Efficiency: Automation of transactions reduces manual data entry, speeding up the supply chain.
Cost Savings: Lower operational costs due to reduced paper usage and fewer errors.
Improved Accuracy: Standardized data exchange minimizes orders, invoices, and shipping notice errors.
Faster Transactions: Real-time data exchange accelerates order processing and payment cycles.
Better Supplier Relationships: Streamlined communication and transparency foster stronger partnerships.
Conclusion
For partners looking to integrate with Circle K’s EDI system, understanding these elements is essential for a successful collaboration that drives mutual growth and efficiency.
Laceup, with its extensive experience in integrating EDI and DEX procedures into Warehouse and DSD systems, is well-equipped to guide you. If you want to learn more, give us your information to schedule a meeting.
I hope this article has been helpful to you. I will continue to post information related to warehouse management, distribution practices and trends, and the economy in general. Our channel has a lot of relevant information. Check out this video on why Retail chains are forcing distributors to use EDI and DEX.


Sorry, the comment form is closed at this time.