
How Agentic AI Is Moving to Run Your Distribution Operation
In the rapidly evolving world of artificial intelligence, we have all become familiar with tools like ChatGPT or Gemini that can generate text, images, or even code based on our prompts. These systems have revolutionized how we create content and brainstorm ideas. But what if AI In Distrution could do more than respond to questions? Enter Agentic AI, the next frontier that is shifting AI from passive conversation to active problem-solving. This transition is already affecting industries across supply chain management, risk assessment, and logistics. In this article, I explore what this shift means, highlight key examples, and look at what’s ahead.
What is Agentic AI? The Proactive Evolution
Agentic AI builds on generative foundations but adds layers of autonomy, reasoning, and action. These systems are designed to pursue specific goals with minimal human intervention, adapting to changes and making decisions along the way. Think of them as digital agents that can plan, execute, and iterate—like a virtual assistant that doesn’t just suggest a plan but carries it out.
At its core, an active AI incorporates:
- Reasoning and Planning: It breaks down complex goals into steps, using iterative thinking to refine approaches.
- Tool Integration: Agents can interact with external systems, APIs, or databases to perform actions.
- Adaptability: Unlike rigid scripts, they handle uncertainty and learn from outcomes to improve.
Key Differences: Generative vs. Agentic AI
To clarify the evolution, here’s a quick comparison:
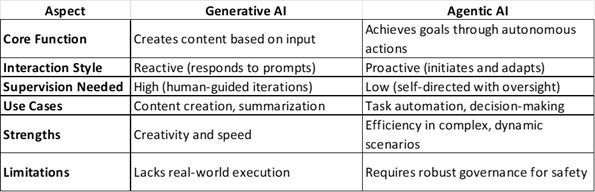
An active AI addresses generative limitations by adding “agency,” enabling it to handle evolving situations. For businesses, this means moving from AI as a tool to AI as a teammate.
Real-World Applications: AI in Action
An active AI is already transforming operations in practical ways. Let’s dive into the examples you mentioned, drawing from emerging implementations.
Evaluating Suppliers
In procurement, active AI agents automate supplier performance reviews by analyzing vast datasets, including delivery times, quality metrics, costs, and even external factors such as market trends and financial stability. Tools like those from JAGGAER or Akira AI can autonomously score suppliers, flag under performers, and recommend alternatives. For example, an AI agent might integrate with ERP systems to monitor ongoing contracts, predict disruptions, and even initiate negotiations. This reduces manual effort, enhances decision-making, and strengthens supply chains.
Monitoring Risks
Business risks, from cyber threats to compliance issues, require constant vigilance. An active AI excels here by continuously scanning data streams for anomalies. Platforms like Riskonnect and Centraleyes use AI to predict risks, monitor behavior in real time, and suggest mitigations. In finance or healthcare, agents can autonomously detect fraud patterns or regulatory changes, alerting teams before issues escalate. NIST’s AI Risk Management Framework emphasizes governance to ensure these systems are reliable. The result? Proactive risk management that saves time and prevents costly breaches.
Autonomously Rerouting DSD Deliveries
Direct Store Delivery (DSD) involves getting products straight from suppliers to retail shelves, often in perishable goods like beverages or snacks. An active AI optimizes this by dynamically rerouting vehicles based on traffic, weather, or demand shifts. Systems from Descartes or LaceUp Solutions use AI for real-time route planning, integrating with GPS and predictive analytics to minimize delays and fuel costs. In advanced setups, autonomous delivery vehicles (like drones or self-driving trucks) handle last-mile logistics, reducing human error and improving efficiency by 30-40%. This is particularly valuable in urban areas where variables change rapidly.
Benefits and Challenges of Agentic AI
The advantages are clear: increased efficiency, scalability, and innovation. Businesses report faster decision-making, cost savings, and better adaptability in volatile markets. However, challenges include ethical concerns, data privacy, and the need for robust identity management to prevent misuse. As agents become more autonomous, ensuring accountability, through frameworks like those from IBM or UiPath, is crucial conclusion
Conclusion
In conclusion, the move from generative to agentic AI isn’t just an upgrade; it is a paradigm shift toward intelligent, action-oriented systems. For businesses, embracing this means staying competitive in a world where AI doesn’t just chat; it delivers results. If you’re in supply chain, risk management, or logistics, now’s the time to explore how an active AI can transform your operations.
At LaceUp Solutions, we explore how technology transforms distribution, from warehouse management and route optimization to digital sales enablement. Subscribe to the LaceUp Blog for weekly insights on wholesale growth, innovation, and the future of logistics. For more information, please get in touch with us to learn about our solutions.
I hope this article have been helpful. I will continue to post information related to management, distribution practices and trends, and the economy in general. Our channel has a lot of relevant information. Check out this video How AI Can Make a Business 5x More Productive.


Sorry, the comment form is closed at this time.