Are Your Vendors Driving Growth? Key Criteria for Selecting Distributor Vendors
Choosing the right distributor vendors is crucial for ensuring a smooth supply chain, maintaining product quality, and driving overall operational efficiency. Distributor vendors act as intermediaries between manufacturers and end customers, handling logistics, inventory management, and market reach. A poor selection can lead to delays, increased costs, or reputational damage, while a strategic choice can enhance scalability and profitability. In this article, I examine key criteria for evaluating and selecting distributor vendors, drawing on established procurement best practices.
Understanding the Distributor Vendors Selection Process
Before diving into specific criteria, it’s important to outline a structured vendor selection process. This typically begins with identifying your business needs, such as required volume, quality standards, delivery timelines, anticipated growth, and alignment with company culture. Following this, organizations often issue a Request for Information (RFI) or Request for Proposal (RFP) to gather data from potential vendors. Tools like a vendor selection matrix can then be used to compare options systematically, assigning weights to different criteria based on priority. The goal is to create a well-orchestrated process that minimizes risks and maximizes value.
Essential Distributor Vendors Selection Criteria
When evaluating distributor vendors, focus on a balanced set of factors that address both immediate needs and long-term sustainability. Below are key criteria, prioritized based on common industry recommendations.
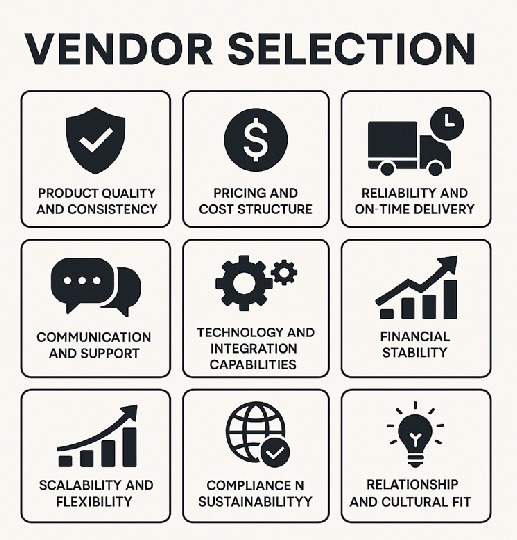
Quality of Products or Services: The cornerstone of any vendor relationship is the quality of what they provide. Ensure the distributor meets technical specifications, offers consistent product quality, and maintains robust quality control processes. This includes certifications such as ISO standards or industry-specific compliance. Poor quality can lead to customer dissatisfaction and returns, eroding trust in your brand.
Cost and Value Proposition: While price is a critical factor, look beyond the sticker price to evaluate the total cost of ownership (TCO). This encompasses transportation costs, payment terms, volume discounts, and any hidden fees. A vendor offering the lowest price might compromise on quality or reliability, so aim for value—reasonable costs aligned with high performance. Compare pricing structures to ensure competitiveness without sacrificing other aspects.
Reliability and Delivery Performance: Reliability is non-negotiable for distributors, who must deliver on time to prevent stockouts or overstocking. Assess their track record for on-time delivery, order accuracy, and ability to handle fluctuations in demand. Factors like lead times, inventory management capabilities, and contingency plans for disruptions should be scrutinized.
Financial Conditions: Financial health is key to mitigating risk and optimizing your own cash flow.
- Financial Stability: Partnering with a financially sound vendor reduces the risk of disruptions due to unforeseen circumstances. Conduct a basic financial due diligence check to assess their ability to meet contractual obligations.
- Cash Conversion Cycle (CCC): This metric determines how much of your cash is tied up in the sales process, and your vendor’s terms directly impact it. The standard formula remains:
CCC = Days Inventory Outstanding (DIO) + Days Sales Outstanding (DSO – Days Payable Outstanding (DPO)
- Strategic Payment Terms: A long Days Payable Outstanding (DPO) (the time you take to pay your vendor) is generally favorable as it allows you to hold onto your cash longer. A shorter CCC indicates a company is recovering cash faster. Look for vendors that can offer flexible payment terms if your payment record is strong.
Technology and Integration Capabilities: Modern distribution operations depend on digital integration. Vendors should be able to connect with your ERP, WMS, or DSD systems through EDI or API integrations. Real-time visibility into inventory levels, shipment tracking, and invoicing accuracy can significantly improve operational efficiency. Look for:
- EDI/API compatibility
- Digital order and invoicing capability
- Real-time data exchange readiness
Compliance and Regulatory Adherence: Distributors must comply with relevant laws, regulations, and ethical standards, including environmental, labor, and trade requirements. This is especially important in global supply chains where non-compliance can result in legal penalties or reputational harm. Verify certifications and audit reports to confirm adherence.
Location and Logistics Capabilities: Geographic proximity can reduce shipping times and costs, making location a key criterion. Consider vendors with strategic warehouses or distribution networks that align with your market reach. Additionally, assess their logistics technology, such as tracking systems and integration with your ERP software.
Sustainability and Ethical Practices: Increasingly, businesses prioritize vendors with strong sustainability initiatives, such as eco-friendly sourcing, reduced carbon footprints, and social responsibility. Evaluate their environmental policies, waste management, and commitment to ethical labor practices. This not only aligns with corporate social responsibility (CSR) goals but can also appeal to eco-conscious customers.
Risk Management and Resilience: Evaluate how vendors mitigate risks, including supply chain disruptions, geopolitical issues, or natural disasters. Look for diversified sourcing, insurance coverage, and business continuity plans. This ensures resilience in volatile markets.
Communication and Customer Service: Effective communication fosters strong partnerships. Assess the vendor’s responsiveness, transparency, and support infrastructure. Traits like transparent reporting, dedicated account managers, and proactive problem-solving are indicators of good service.
Best Practices for Implementation
To apply these criteria effectively, use a scoring system in your vendor matrix, where each factor is weighted according to your priorities (e.g., quality at 25%, cost at 20%). Conduct site visits, reference checks, and pilot tests before finalizing. Regularly review selected vendors through performance metrics to ensure ongoing alignment.
Conclusion
Selecting the right distributor vendors requires a comprehensive evaluation of multiple criteria to balance short-term gains with long-term success. By focusing on quality, cost, reliability, and emerging factors like sustainability and digital innovation, businesses can build resilient supply chains that support growth. Remember, the ideal vendor is not just a supplier but a strategic partner invested in your success. Adopting a methodical approach will help mitigate risks and optimize outcomes in an ever-evolving market.
At LaceUp Solutions, we explore how technology transforms distribution, from warehouse management and route optimization to digital sales enablement. Subscribe to the LaceUp Blog for weekly insights on wholesale growth, innovation, and the future of logistics. For more information, please get in touch with us to learn about our solutions.
I hope this article on how to Increase Wholesale Sales have been helpful. I will continue to post information related to management, distribution practices and trends, and the economy in general. Our channel has a lot of relevant information. Check out this video on “Vendor Selection”.
I hope this article on how to Increase Wholesale Sales have been helpful. I will continue to post information related to management, distribution practices and trends, and the economy in general. Our channel has a lot of relevant information. Check out this video on “Vendor Selection”.


Sorry, the comment form is closed at this time.