
Blockchain in Food industry: Ensuring Transparency-Safety
When people hear the word “Blockchain” they relate it to Cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin (BTC) or Ethereum (ETH). But in an age where consumers demand more transparency about the origin, safety, and authenticity of the food they consume, blockchain is emerging as a powerful tool to transform how we source, track, and deliver food. In this article, I explore the profound impact of blockchain in food industry, from ensuring food safety to enhancing supply chain transparency.
Blockchain in food industry: How does it work?
We have already written about blockchain principles in Blockchain Technology Impact on the Distribution Industry (Part I). But how does it work in the food industry? Blockchain in food industry is built around a distributed ledger that contains data on all food supply chain transactions and events. The ledger is formed by timestamped and encrypted data blocks linked in chronological order. Each block holds a batch of transactions validated based on the pre-defined consensus protocol. Food supply chain participants interact with the blockchain ledger using the role-specific web and/or mobile applications.
Blockchain in food industry: Ensuring Food Safety
Food safety is paramount in the food industry, and blockchain is a potent tool to achieve this. Blockchain technology enables the comprehensive tracking and tracing of food products at every stage of their journey. Here’s how:
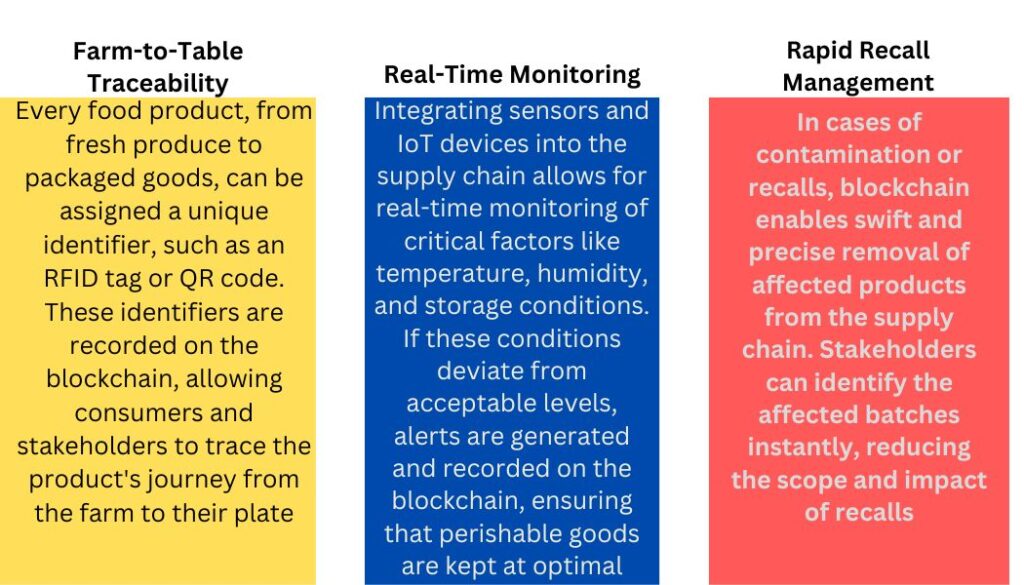
Enhancing Transparency
Consumers are increasingly seeking transparency about the origin, quality, and ethical sourcing of their food. And the FDA is reinforcing that with its Food Traceability Rule to get in effect by 2025. Blockchain addresses this demand by providing:
Accessible Information: Anyone, from consumers to regulators, can access the blockchain to verify the authenticity and source of a food product. This transparency builds trust and confidence in the food supply chain.
Supply Chain Visibility: All participants in the supply chain, including farmers, processors, distributors, and retailers, can access a shared ledger that updates in real time. This eliminates information asymmetry and reduces disputes.
Ethical Sourcing: Blockchain can be used to track the ethical and sustainable sourcing of ingredients, allowing consumers to make informed choices that align with their values.
Blockchain in food industry: Mitigating Food Fraud and Counterfeiting
Food fraud, which includes mislabeling and counterfeiting of food products, is a significant concern in the industry. Blockchain’s tamper-proof ledger makes it exceedingly difficult for fraudulent activities to go undetected. By recording every step of a food product’s journey, blockchain ensures that consumers receive genuine, high-quality products.
Operational Efficiency and Cost Savings
In addition to improving safety and transparency, blockchain in food industry enhances operational efficiency:
- Reduced Administrative Overhead: Automating the documentation, compliance, and quality control processes reduces administrative costs and paperwork.
- Faster Transactions: Blockchain enables faster and more efficient transactions, ensuring that food products reach their destination promptly.
- Lower Risk: The immutability of blockchain data minimizes the risk of disputes, recalls, and financial losses due to fraudulent activities.
Who is currently utilizing blockchain technology within the food industry?
Bumblebee Foods, Tyson Foods, Kraft Heinz, Nestlé, and Walmart all are currently utilizing or testing out BT.
Bumble Bee Foods utilizes BT to record its tuna operations and to improve product traceability while deterring acts of food fraud. Products are traced through the supply chain from catch to sales.
Walmart has been utilizing BT to digitize their food product supply chain to enhance Tech-Enabled Traceability and to reduce the time it takes to track the source of food contamination. Walmart requires all trading suppliers of leafy-green vegetables to comply with data record input into a system blockchain platform which can trace-back their produce. They now can trace the source of contaminated produce within seconds.
Tyson Foods is using BT management to trace their supply chain from farms to their production facilities. Tyson is currently partnering with a platform FoodLogiQ on a food safety pilot project.
Kraft Heinz is also utilizing blockchain technology with their children’s foods division. They are working to implement a traceability system through BT.
I hope this article about blockchain in food industry has been helpful to you. I will continue to post information related to warehouse management, distribution practices and trends, and the economy in general. If you are interested in learning more, click the link, and we will call you.
There is a lot of relevant information on our channel. Check this video on How To REDUCE Turnover in YOUR Warehouse.


Sorry, the comment form is closed at this time.