
Surviving Volume Volatility in Distribution Centers
Distribution centers are the beating heart of logistics operations. They handle the flow of goods from suppliers to customers, ensuring timely deliveries and efficient inventory turnover. However, one of the most persistent challenges in this field is volume volatility. For warehouse managers and operators, surviving these swings isn’t just about endurance; it is about strategic adaptation to maintain service levels, control costs, and keep operations running smoothly. This article explores the nature of volume volatility in distribution, its impacts, and proven strategies to thrive amid the chaos.
Understanding Volume Volatility in Distribution
Volume volatility refers to the erratic changes in the volume of inbound and outbound goods within a distribution network. Unlike steady, predictable flows, volatility introduces peaks that can overwhelm facilities and valleys that underutilize resources. For instance, e-commerce giants often experience massive surges during events like Black Friday or the holiday season, when order volumes can double or triple overnight. On the flip side, slowdowns might occur due to supplier delays or market slumps.. On the flip side, slowdowns might occur due to supplier delays or market slumps.
Historically, many distribution models have been designed around average daily volumes, using historical data to forecast space, labor, and equipment needs. But averages can be misleading. Real-world operations are characterized by concentrated bursts of activity rather than uniform distribution. A single late truckload or a viral product promotion can compress hours of work into a narrow window, pushing facilities beyond their comfort zones. In 2025, with the rise of omnichannel retailing and just-in-time inventory practices, these fluctuations have only intensified, making volatility a standard operating condition rather than an anomaly.
The Impacts of Unmanaged Volume Volatility in Distribution
When volume spikes hit unprepared, the ripple effects can be severe. Inbound surges create bottlenecks at receiving docks. These delays put away processes, cluttering aisles, and increasing travel times for pickers. On the outbound side, compressed shipping windows heighten the risk of errors, missed cutoffs, and carrier penalties. Facilities operating at 110% or more of their typical capacity often see productivity plummet as congestion turns efficient layouts into obstacles.
The human element suffers too. Staff may be required to work extended hours, leading to fatigue and higher error rates. Equipment strain increases maintenance costs, and inventory inaccuracies can snowball into stockouts or overstocks. Financially, the toll is steep: emergency overtime, temporary hires, rented trailers, and expedited shipping fees can erode margins. In extreme cases, repeated failures can damage customer trust and lead to lost business. Conversely, during low-volume periods, idle resources represent wasted potential, from underused space to excess labor costs.
Strategies for Building Resilience to Volume Volatility in Distribution
Surviving volume volatility requires a proactive mindset, shifting from reactive firefighting to resilient design. Here are key strategies to fortify your distribution operations:
1. Identify and Reinforce Bottlenecks
Start by mapping your facility’s flow and pinpointing the first point of failure during peaks. Is it dock capacity, replenishment speed, or sortation throughput? Use data analytics from warehouse management systems (WMS) to simulate scenarios and stress-test processes. Once identified, bolster these areas—perhaps by adding flexible docking bays or optimizing put-away algorithms. Regular audits ensure these reinforcements evolve with changing demands.
2. Embrace Elasticity in Design and Operations
Elasticity is the cornerstone of volatility-proof distribution. Design warehouses with buffer zones: reserve storage for overflow inventory, expandable staging areas for outbound rushes, and wider aisles to accommodate denser equipment traffic. Implement dynamic slotting, where high-velocity items are repositioned based on real-time data, such as during promotions.
Labor flexibility is equally crucial. Cross-train teams to shift seamlessly between receiving, picking, packing, and shipping roles. Flexible scheduling, including part-time or on-call workers, helps scale staffing without permanent overhead. In 2025, AI-driven workforce management tools can predict surges and automate shift adjustments, minimizing disruptions.
3. Leverage Technology and Automation
Automation acts as a stabilizer in volatile environments. Goods-to-person systems reduce manual travel, maintaining throughput even under heavy loads. Automated sorters and conveyor belts handle increased carton volumes without corresponding increases in labor. A robust WMS is essential: ensure it can handle high transaction volumes without lag, with features such as real-time task prioritization and predictive analytics.
Internet of Things (IoT) sensors can monitor equipment health and inventory levels, alerting teams to impending issues. For example, integrating AI forecasting with supplier data can anticipate inbound spikes, allowing preemptive adjustments.
4. Foster Strong Supplier and Carrier Relationships
Volatility often originates upstream or downstream. Collaborate with suppliers to improve shipment visibility, using shared platforms for real-time tracking. Negotiate flexible contracts that incentivize steady deliveries, such as volume-based discounts. On the carrier side, diversify partnerships to avoid single-point failures and build in contingency plans for peak periods.
5. Plan for Costs and Contingencies
Proactive preparation is more cost-effective than crisis response. Budget for peak scenarios by allocating funds for temporary resources in advance. Conduct regular drills to test volatility responses, refining plans based on outcomes. Measure success through key performance indicators (KPIs). Old metrics fail in unstable environments. Use these metrics instead.
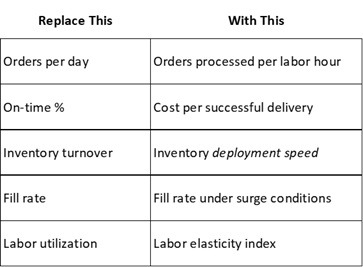
Conclusion
Volume volatility in distribution is inevitable, but suffering from it is optional. By designing operations around peaks rather than averages, investing in elasticity, and harnessing technology, facilities can achieve consistent performance even in turbulent times. The payoff is multifaceted: lower costs, higher service levels, and a competitive edge in a market that rewards agility. As supply chains continue to evolve in 2025 and beyond, those who master volatility won’t just survive—they’ll lead. Whether you’re managing a small warehouse or a global network, the time to build resilience is now, before the next surge hits.
At LaceUp Solutions, we explore how technology transforms distribution, from warehouse management and route optimization to digital sales enablement. Subscribe to the LaceUp Blog for weekly insights on wholesale growth, innovation, and the future of logistics. For more information, please get in touch with us to learn about our solutions.
I hope this article about Volume volatility in distribution have been helpful. I will continue to post information related to management, distribution practices and trends, and the economy in general. Our channel has a lot of relevant information. Check out this video about the hardest things to implement in a WMS.


Sorry, the comment form is closed at this time.