The Crucial Role of Quality Control in Distribution
Maintaining high-quality standards is paramount in the distribution and wholesale industry. Quality control is crucial in ensuring that products meet or exceed customer expectations. This article delves into the significance of quality control in distribution and wholesale operations, highlighting its benefits, sensible processes, and critical quality control practices.
Importance of Quality Control in Distribution
Implementing quality control practices enhances the supply chain’s overall efficiency. Companies can improve operational efficiency in four main areas by minimizing defects and ensuring product consistency.
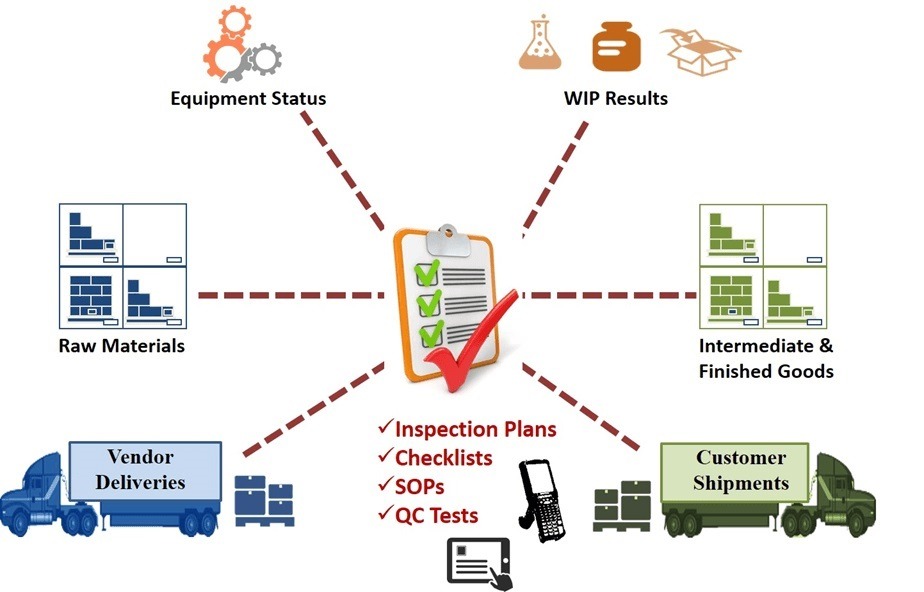
Distribution processes Sensible to quality issues
Several processes within a distribution operation require quality control to ensure that products meet or exceed customer expectations. Some key processes include:
Receiving and Inspection: Goods received from suppliers should be inspected for quality and accuracy. This inspection includes checking for damage, verifying quantities, and ensuring that products meet specifications.
Storage and Handling: Proper storage and handling practices are essential to maintaining product quality. These practices include maintaining proper temperature and humidity levels, ensuring products are stored correctly to prevent damage, and following proper handling procedures to avoid contamination.
Picking and Packing: When orders are picked and packed for shipping, it is important to ensure that the correct products are selected, that they are in good condition, and that they are packed securely to prevent damage during transit.
Shipping and Transportation: Quality control in shipping and transportation involves ensuring products are shipped in a timely manner, protected from damage during transit, and delivered to the correct location.
Inventory Management: Your diligent implementation of proper inventory management practices is key to ensuring product quality. This includes maintaining accurate inventory records, implementing FIFO (first in, first out) or FEFO (first expired, first out) inventory systems for perishable goods, and regularly auditing inventory to identify and address discrepancies.
Returns and Customer Complaints: Handling returns and customer complaints is integral to quality control. This process involves investigating the root causes of returns and complaints, addressing any issues, and implementing corrective actions to prevent recurrence.
Quality Control Strategies for Quality Control in Distribution Processes
In this section, we list the quality control measures for each process in a distribution operation that will prevent you from delivering defective or incorrect products to your customers.
Receiving and Inspection:
- Conduct thorough inspections of incoming goods based on predetermined quality criteria.
- Use quality control checklists to ensure all aspects of the received products are inspected.
- Implement sampling techniques for large shipments to ensure representative inspection.
- Train the receiving personnel on proper inspection techniques and quality standards.
Storage and Handling:
- Implement proper storage practices, such as maintaining correct temperature and humidity levels.
- Use appropriate storage equipment (e.g., pallets and shelves) to prevent product damage.
- Regularly inspect storage areas for cleanliness and organization.
- Train warehouse staff on proper handling procedures to minimize product damage.
Picking and Packing:
- Use barcoding or RFID technology to ensure accurate picking of products.
- Implement double-check procedures to verify that the correct products are being picked.
- Use appropriate packaging materials to protect products during transit.
- Conduct regular audits of picking and packing processes to identify and address any issues.
Shipping and Transportation:
- Use reputable carriers with a track record of reliable and safe transportation.
- Ensure products are properly packaged and secured for transit.
- Monitor temperature and humidity levels during transportation for temperature-sensitive products.
- Implement tracking systems to monitor the location and condition of products during transit.
Inventory Management:
- Use inventory management software to track inventory levels and movement accurately.
- Implement regular cycle counting and reconciliation processes to identify and correct inventory discrepancies.
- Use RFID or barcoding technology to improve inventory accuracy and reduce errors.
- Implement strict inventory control policies to prevent stockouts and overstock situations.
Returns and Customer Complaints:
- Implement a returns management process to handle returned products efficiently.
- Investigate the root causes of returns and customer complaints to identify quality issues.
- Implement corrective actions to address identified quality issues and prevent recurrence.
- Use customer feedback to improve products and processes continuously.
Conclusion
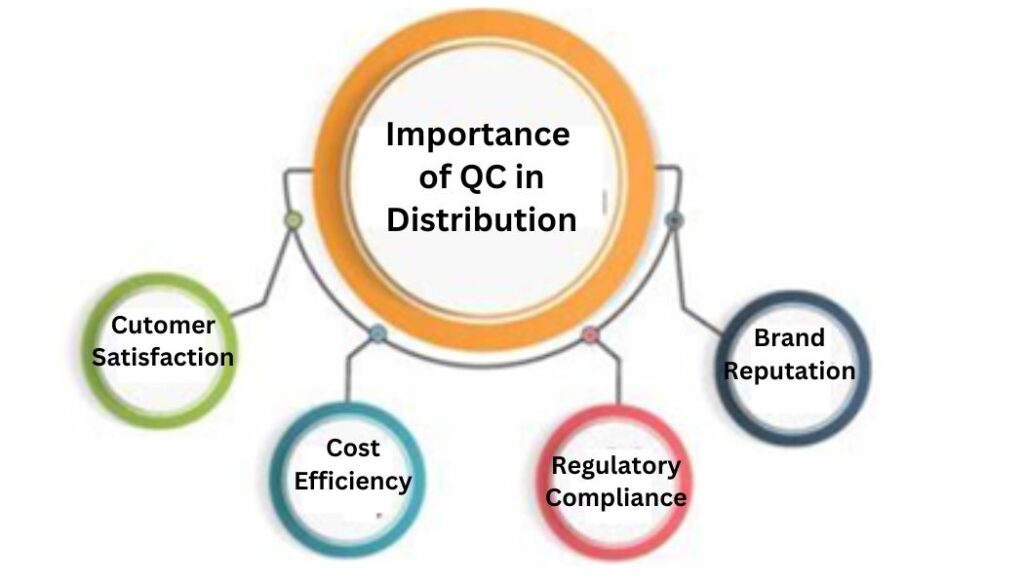
Quality control is critical to distribution and wholesale operations, impacting customer satisfaction, cost efficiency, regulatory compliance, and brand reputation. Companies can achieve and maintain high-quality standards by implementing robust quality control measures and continuously improving them, ensuring long-term success in the competitive marketplace. Our WMS, Route, and DSD solutions provide the tools to monitor your quality control metrics. If you want to learn more, give us your information so we can schedule a meeting.
I hope this article about quality control in distribution has been helpful to you. I will continue to post information related to warehouse management, distribution practices and trends, and the economy in general. Our channel has a lot of relevant information. Check out this video on Guide To FDA Inspections & Food Recalls.


Sorry, the comment form is closed at this time.